Microsoft’s Active Directory Security Feature
Microsoft’s Active Directory Security Feature
Read More
For active directory, Kerberos was used.
Kerberos is automatically installed when the Active Directory is installed on a Windows 2000 DC. It is used for user logon authentication and also to support transitive trusts in Windows 2000.
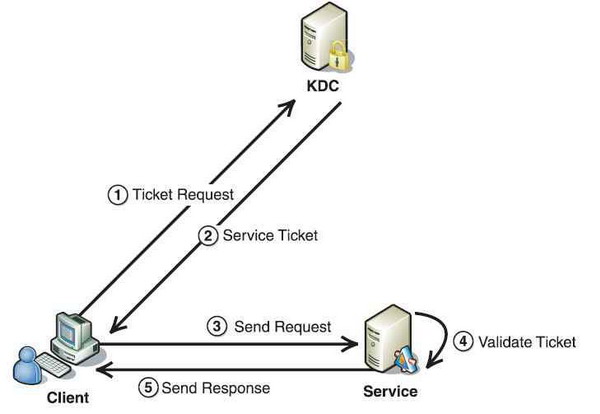
The physical components of Kerberos are client, server and key distribution center (KDC). Kerberos authencation process is the result of an interaction between the client requesting a service, the server providing a service and the KDC, a key server that distribute keys.
For enhance security, three keys are needed in order to provide a much secured interaction among client, server and KDC. The three keys are session key, client key and server key.

The process is as follow:
- The client will request access to a server service
- The KDC creates the session key
- The KDC creates a ticket and encrypts it with a key
- The client decrypts the response with the key and extracts the ticket.
- The client sends an application request to the server and a ticket encrypted with a key
- The server decrypts the ticket with its key and gets the session key
- The server uses the session key to decrypt the authenticator




